Operations Examples¶
move¶
Move a Point:
>>> a = Point(1,2,1)
>>> print('a before move:{}'.format(a))
a before move:Point(1, 2, 1)
>>> a.move(x_unit_vector())
Point(2, 2, 1)
>>> print('a after move:{}'.format(a))
a after move:Point(2, 2, 1)
Move a Segment:
>>> b = origin()
>>> c = Point(1,2,3)
>>> s = Segment(b,c)
>>> s
Segment(Point(0, 0, 0), Point(1, 2, 3))
>>> s.move(Vector(-1,-2,-3))
Segment(Point(-1, -2, -3), Point(0, 0, 0))
>>> s
Segment(Point(-1, -2, -3), Point(0, 0, 0))
Move a ConvexPolygon Without Changing the Original Object:
>>> import copy
>>> cpg0 = Parallelogram(origin(),x_unit_vector(),y_unit_vector())
>>> cpg0
ConvexPolygon((Point(0, 0, 0), Point(1, 0, 0), Point(1, 1, 0), Point(0, 1, 0)))
>>> cpg1 = copy.deepcopy(cpg0).move(Vector(0,0,1))
>>> cpg0
ConvexPolygon((Point(0, 0, 0), Point(1, 0, 0), Point(1, 1, 0), Point(0, 1, 0)))
>>> cpg1
ConvexPolygon((Point(0, 0, 1), Point(1, 0, 1), Point(1, 1, 1), Point(0, 1, 1)))
Intersection¶
The operation of intersection is very complex. There are a total of 21 situations.
obj1 |
obj2 |
output obj |
|---|---|---|
Point |
Point |
None, Point |
Point |
Line |
None, Point |
Point |
Plane |
None, Point |
Point |
Segment |
None, Point |
Point |
ConvexPolygon |
None, Point |
Point |
ConvexPolyhedron |
None, Point |
Point |
HalfLine |
None, Point |
Line |
Line |
None, Point, Line |
Line |
Plane |
None, Point, Line |
Line |
Segment |
None, Point, Segment |
Line |
ConvexPolygon |
None, Point, Segment |
Line |
ConvexPolyhedron |
None, Point, Segment |
Line |
HalfLine |
None, Point, HalfLine |
Plane |
Plane |
None, Line, Plane |
Plane |
Segment |
None, Point, Segment |
Plane |
ConvexPolygon |
None, Point, Segment, ConvexPolygon |
Plane |
ConvexPolyhedron |
None, Point, Segment, ConvexPolygon |
Plane |
HalfLine |
None, Point, HalfLine |
Segment |
Segment |
None, Point, Segment |
Segment |
ConvexPolygon |
None, Point, Segment |
Segment |
ConvexPolyhedron |
None, Point, Segment |
Segment |
HalfLine |
None, Point, Segment |
ConvexPolygon |
ConvexPolygon |
None, Point, Segment, ConvexPolygon |
ConvexPolygon |
ConvexPolyhedron |
None, Point, Segment, ConvexPolygon |
ConvexPolygon |
HalfLine |
None, Point, Segment |
ConvexPolyhedron |
ConvexPolyhedron |
None, Point, Segment, ConvexPolygon, ConvexPolyhedron |
ConvexPolyhedron |
HalfLine |
None, Point, Segment |
HalfLine |
HalfLine |
None, Point, Segment, HalfLine |
All of the situations above are implemented. The documentation shows some examples.
Example 1:
>>> po = origin()
>>> l1 = x_axis()
>>> l2 = y_axis()
>>> intersection(po,l1)
Point(0, 0, 0)
>>> intersection(l1,l2)
Point(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
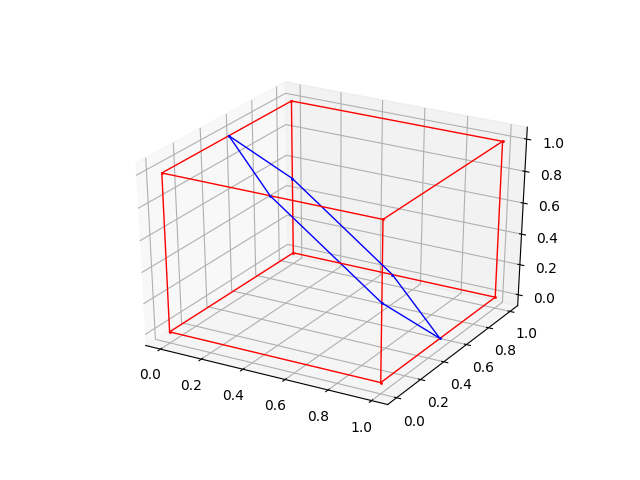
>>> s1 = Segment(Point(1,0,1),Point(0,1,1))
>>> s2 = Segment(Point(0,0,1),Point(1,1,1))
>>> s3 = Segment(Point(0.5,0.5,1),Point(-0.5,1.5,1))
>>> intersection(s1,s2)
Point(0.5, 0.5, 1.0)
>>> intersection(s1,s3)
Segment(Point(0.5, 0.5, 1.0), Point(0, 1, 1))
>>> intersection(l1,s1) is None
True
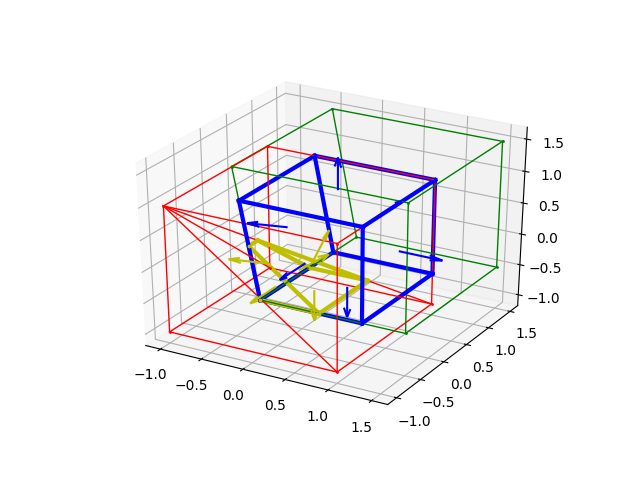
>>> cph0 = Parallelepiped(origin(),x_unit_vector(),y_unit_vector(),z_unit_vector())
>>> p = Plane(Point(0.5,0.5,0.5),Vector(1,1,1))
>>> cpg = intersection(cph0,p)
>>> r = Renderer()
>>> r.add((cph0,'r',1),normal_length = 0)
>>> r.add((cpg,'b',1),normal_length=0)
>>> r.show()
Example 2:
>>> from Geometry3D import *
>>> import copy
>>> r = Renderer()
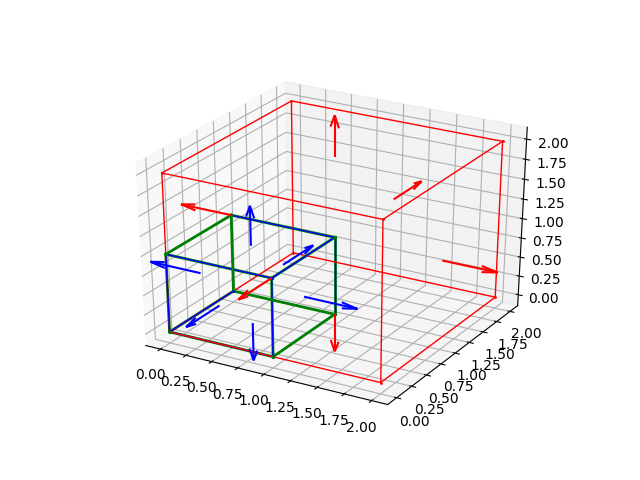
>>> cph0 = Parallelepiped(origin(),x_unit_vector(),y_unit_vector(),z_unit_vector())
>>> cph6 = Parallelepiped(origin(),2 * x_unit_vector(),2 * y_unit_vector(),2 * z_unit_vector())
>>> r.add((cph0,'b',1),normal_length = 0.5)
>>> r.add((cph6,'r',1),normal_length = 0.5)
>>> r.add((intersection(cph6,cph0),'g',2))
>>> print(intersection(cph0,cph6))
ConvexPolyhedron
pyramid set:{Pyramid(ConvexPolygon((Point(1, 1, 1), Point(0, 1, 1), Point(0.0, 0.0, 1.0), Point(1, 0, 1))), Point(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)), Pyramid(ConvexPolygon((Point(1.0, 0.0, 0.0), Point(1, 0, 1), Point(1, 1, 1), Point(1, 1, 0))), Point(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)), Pyramid(ConvexPolygon((Point(1, 1, 0), Point(1, 1, 1), Point(0, 1, 1), Point(0.0, 1.0, 0.0))), Point(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)), Pyramid(ConvexPolygon((Point(0, 0, 1), Point(0, 0, 0), Point(0, 1, 0), Point(0, 1, 1))), Point(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)), Pyramid(ConvexPolygon((Point(1, 0, 0), Point(1, 0, 1), Point(0, 0, 1), Point(0, 0, 0))), Point(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)), Pyramid(ConvexPolygon((Point(1, 1, 0), Point(1, 0, 0), Point(0, 0, 0), Point(0, 1, 0))), Point(0.5, 0.5, 0.5))}
point set:{Point(1, 1, 0), Point(1, 1, 1), Point(0, 0, 1), Point(0, 1, 0), Point(0, 1, 1), Point(1.0, 0.0, 0.0), Point(0, 0, 0), Point(1, 0, 1)}
>>> r.show()
Example 3:
>>> from Geometry3D import *
>>>
>>> a = Point(1,1,1)
>>> b = Point(-1,1,1)
>>> c = Point(-1,-1,1)
>>> d = Point(1,-1,1)
>>> e = Point(1,1,-1)
>>> f = Point(-1,1,-1)
>>> g = Point(-1,-1,-1)
>>> h = Point(1,-1,-1)
>>> cph0 = Parallelepiped(Point(-1,-1,-1),Vector(2,0,0),Vector(0,2,0),Vector(0,0,2))
>>> cpg12 = ConvexPolygon((e,c,h))
>>> cpg13 = ConvexPolygon((e,f,c))
>>> cpg14 = ConvexPolygon((c,f,g))
>>> cpg15 = ConvexPolygon((h,c,g))
>>> cpg16 = ConvexPolygon((h,g,f,e))
>>> cph1 = ConvexPolyhedron((cpg12,cpg13,cpg14,cpg15,cpg16))
>>> a1 = Point(1.5,1.5,1.5)
>>> b1 = Point(-0.5,1.5,1.5)
>>> c1 = Point(-0.5,-0.5,1.5)
>>> d1 = Point(1.5,-0.5,1.5)
>>> e1 = Point(1.5,1.5,-0.5)
>>> f1 = Point(-0.2,1.5,-0.5)
>>> g1 = Point(-0.2,-0.5,-0.5)
>>> h1 = Point(1.5,-0.5,-0.5)
>>>
>>> cpg6 = ConvexPolygon((a1,d1,h1,e1))
>>> cpg7 = ConvexPolygon((a1,e1,f1,b1))
>>> cpg8 = ConvexPolygon((c1,b1,f1,g1))
>>> cpg9 = ConvexPolygon((c1,g1,h1,d1))
>>> cpg10 = ConvexPolygon((a1,b1,c1,d1))
>>> cpg11 = ConvexPolygon((e1,h1,g1,f1))
>>> cph2 = ConvexPolyhedron((cpg6,cpg7,cpg8,cpg9,cpg10,cpg11))
>>> cph3 = intersection(cph0,cph2)
>>>
>>> cph4 = intersection(cph1,cph2)
>>> r = Renderer()
>>> r.add((cph0,'r',1),normal_length = 0)
>>> r.add((cph1,'r',1),normal_length = 0)
>>> r.add((cph2,'g',1),normal_length = 0)
>>> r.add((cph3,'b',3),normal_length = 0.5)
>>> r.add((cph4,'y',3),normal_length = 0.5)
>>> r.show()